Many trading strategies depend heavily on candle close confirmation, especially setups where entries, exits, or validations are considered reliable only after a candlestick has fully completed its formation.
In such cases, the candlestick close timer, officially called the ‘Countdown to Bar Close’, becomes an essential visual tool. This timer shows how much time remains before the current candle closes, helping traders avoid premature decisions and emotional entries during an unfinished price move.
Why the ‘Countdown to Bar Close’ Sometimes Disappears?
In TradingView, this feature can disappear if chart settings are changed unknowingly while experimenting with customization options.
The candlestick close timer does not vanish due to a system error or platform limitation. In most cases, it is turned off unintentionally when users adjust time scale settings, modify chart preferences, or experiment with visual layouts.
Since TradingView offers extensive chart customization, it is very easy to disable certain display elements without realizing their importance at the moment.
Also Read – 3 Easy Methods to Hide Candlesticks in TradingView
If your candle time is not showing, here are 3 simple methods to enable the candle timer for any timeframe in TradingView.
Method One: Enabling the ‘Countdown to Bar Close’ from Chart Settings
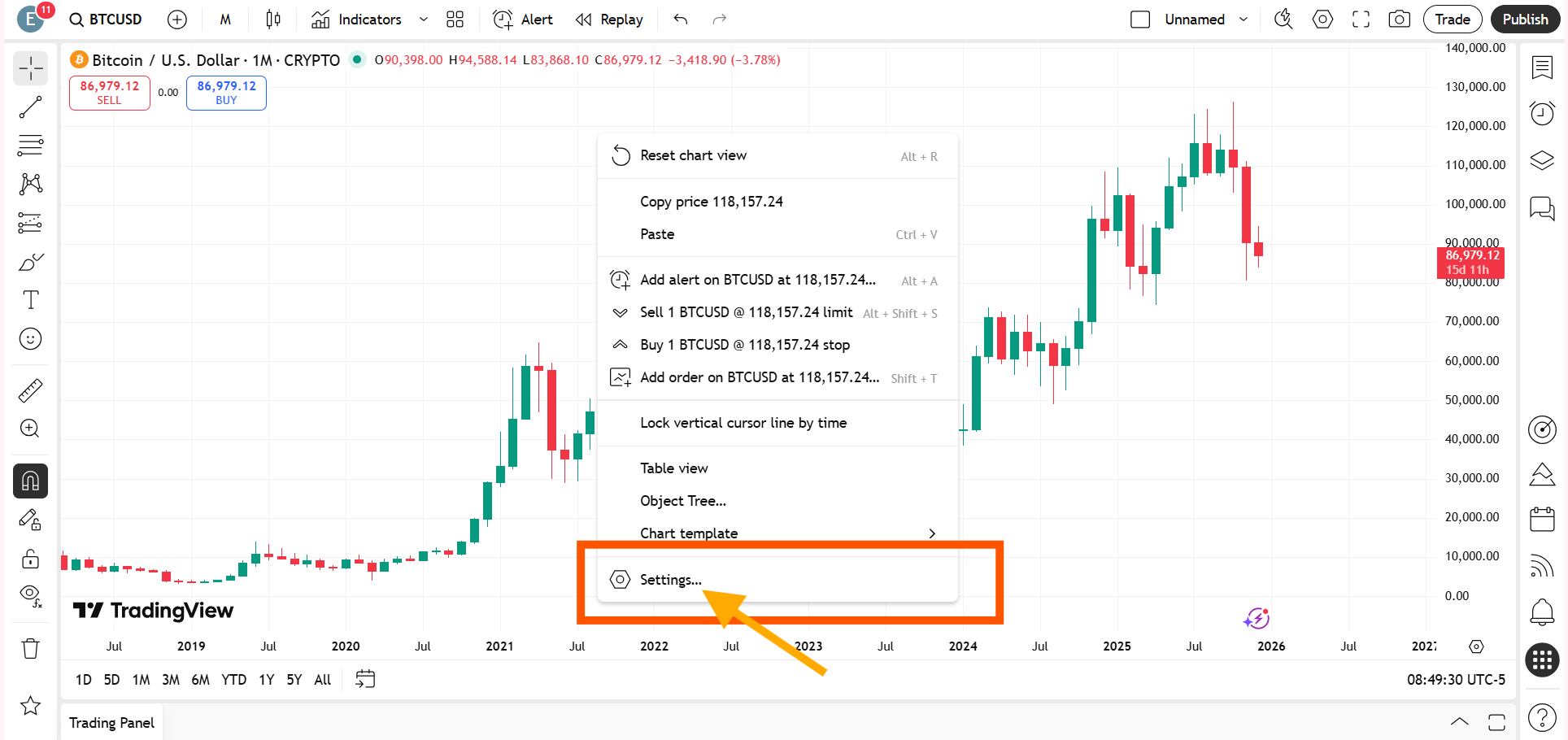
The most direct and controlled way to bring back the candlestick close timer is to enable it manually from the chart settings.
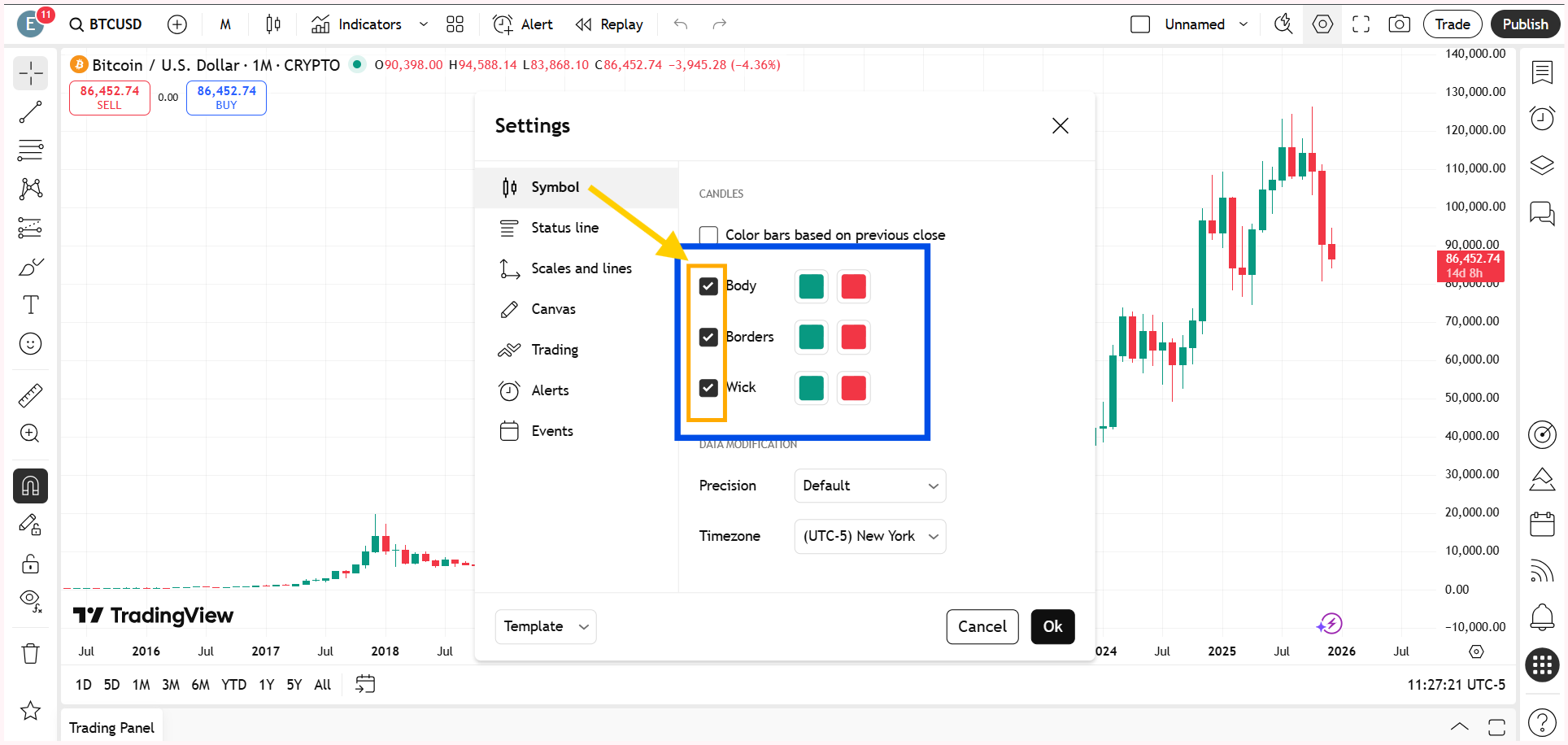
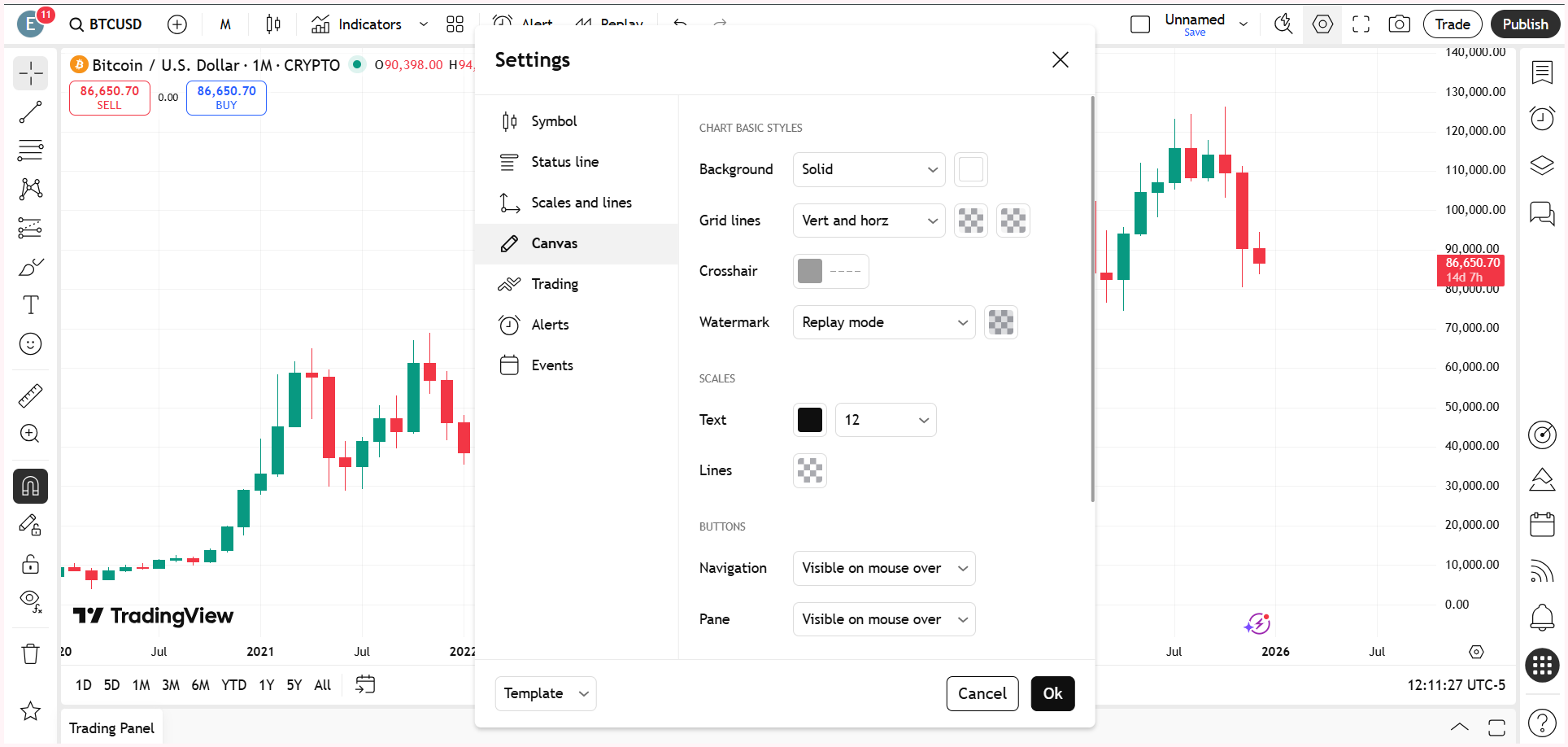
Right-click anywhere on the chart and open Settings. Then go to the Scales and Lines section and look for the option called ‘Countdown to Bar Close.’ Simply tick this option.
Once enabled, the countdown timer immediately appears on the price chart and starts showing the remaining time for the active candlestick on TradingView.
This method is ideal for traders who want to keep their existing chart layout, indicators, and visual preferences unchanged while restoring only the missing timer.

Alternatively, you can access the Scales and Lines option by right-clicking directly on the price scale. Select More Settings, and then follow the same steps under Scales and Lines as explained above.
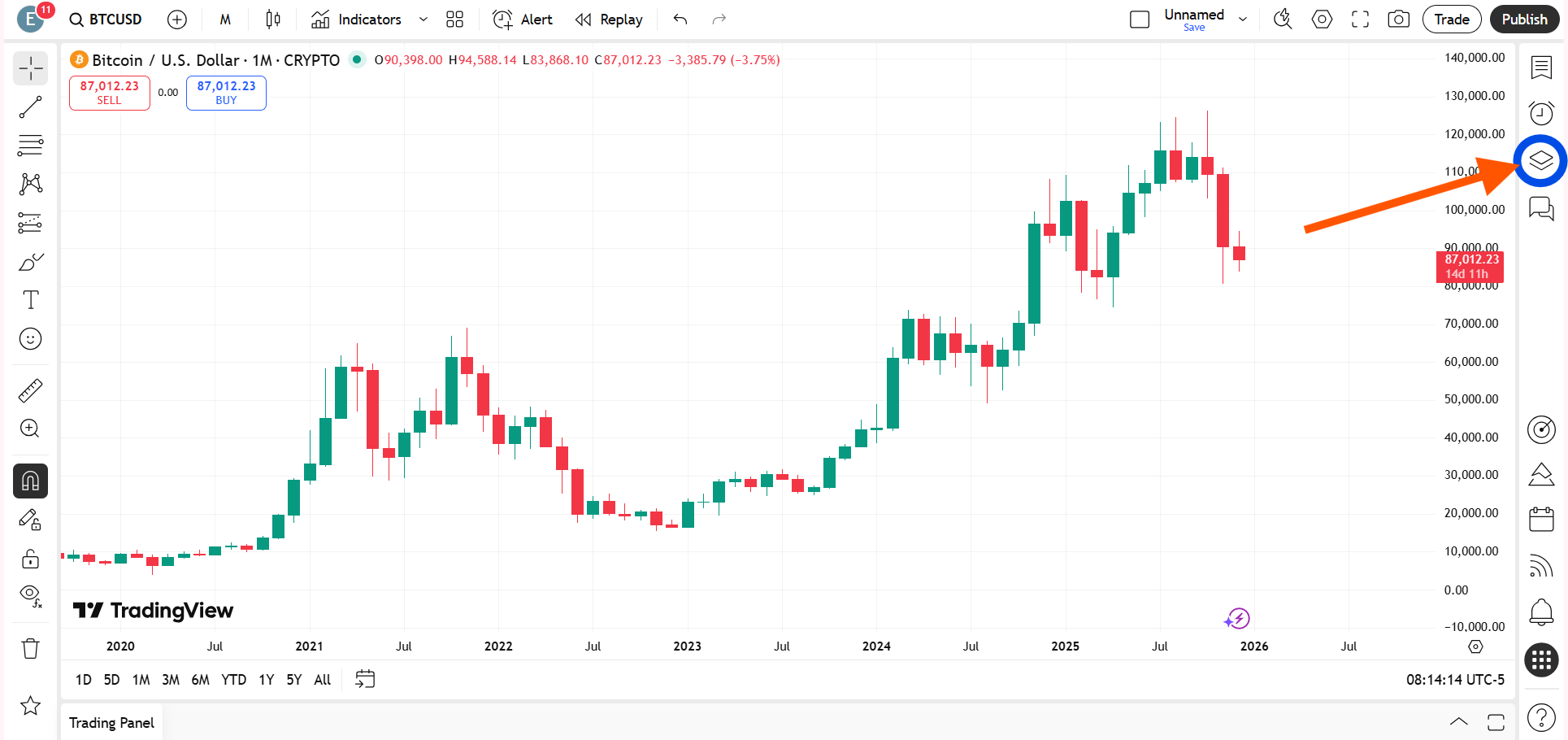
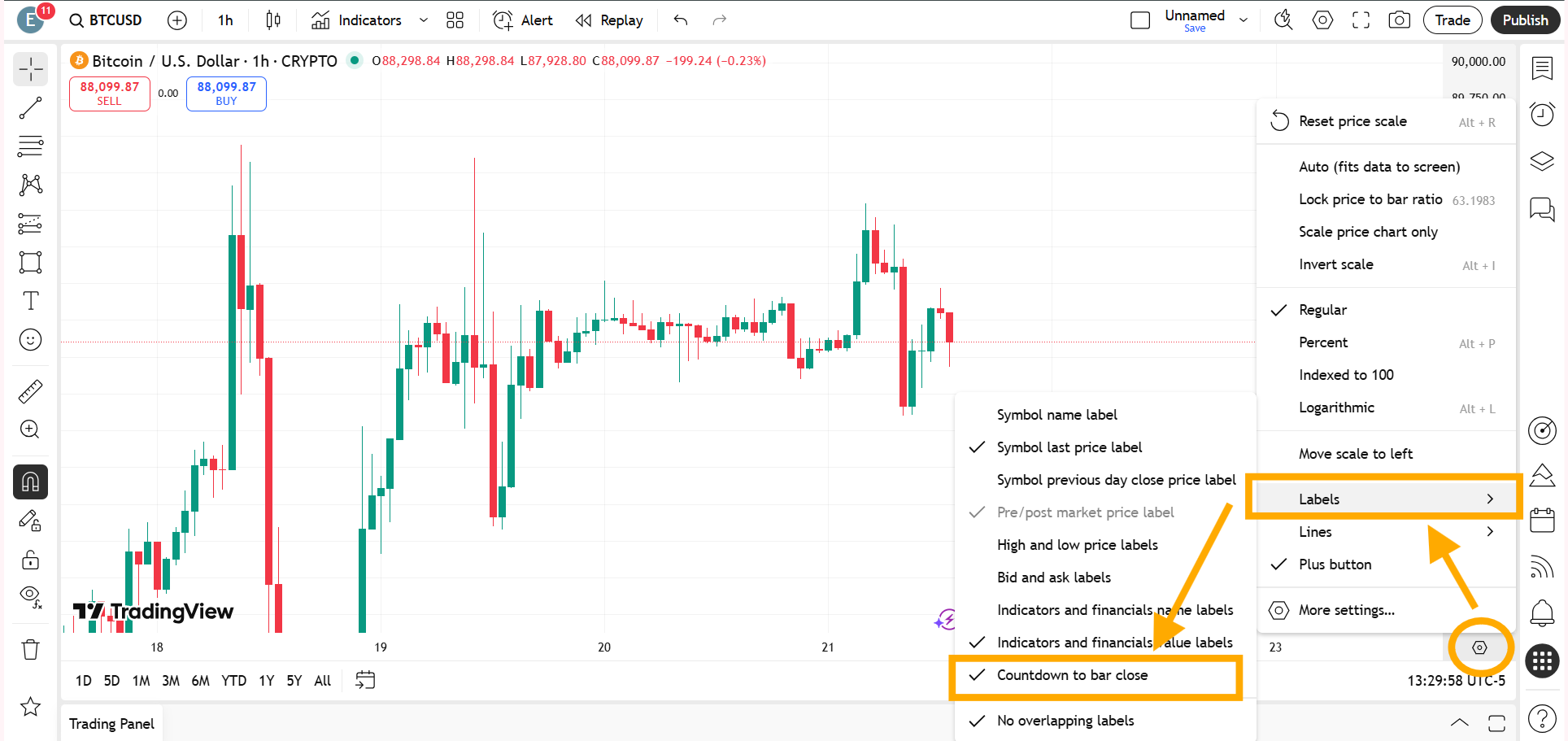
Method Two: Fix Candle Timer from Labels Menu
Click on the settings icon at the bottom of the price scale of the trading instrument and go to Labels.
When you hover your cursor over Labels, several options will appear. Find Countdown to Bar Close and enable it.
Once selected, the timer will start showing again.
Method Three: Restoring the Timer by Resetting the Chart to Default
Another effective way to enable the candlestick close timer is by resetting the chart to its default configuration.
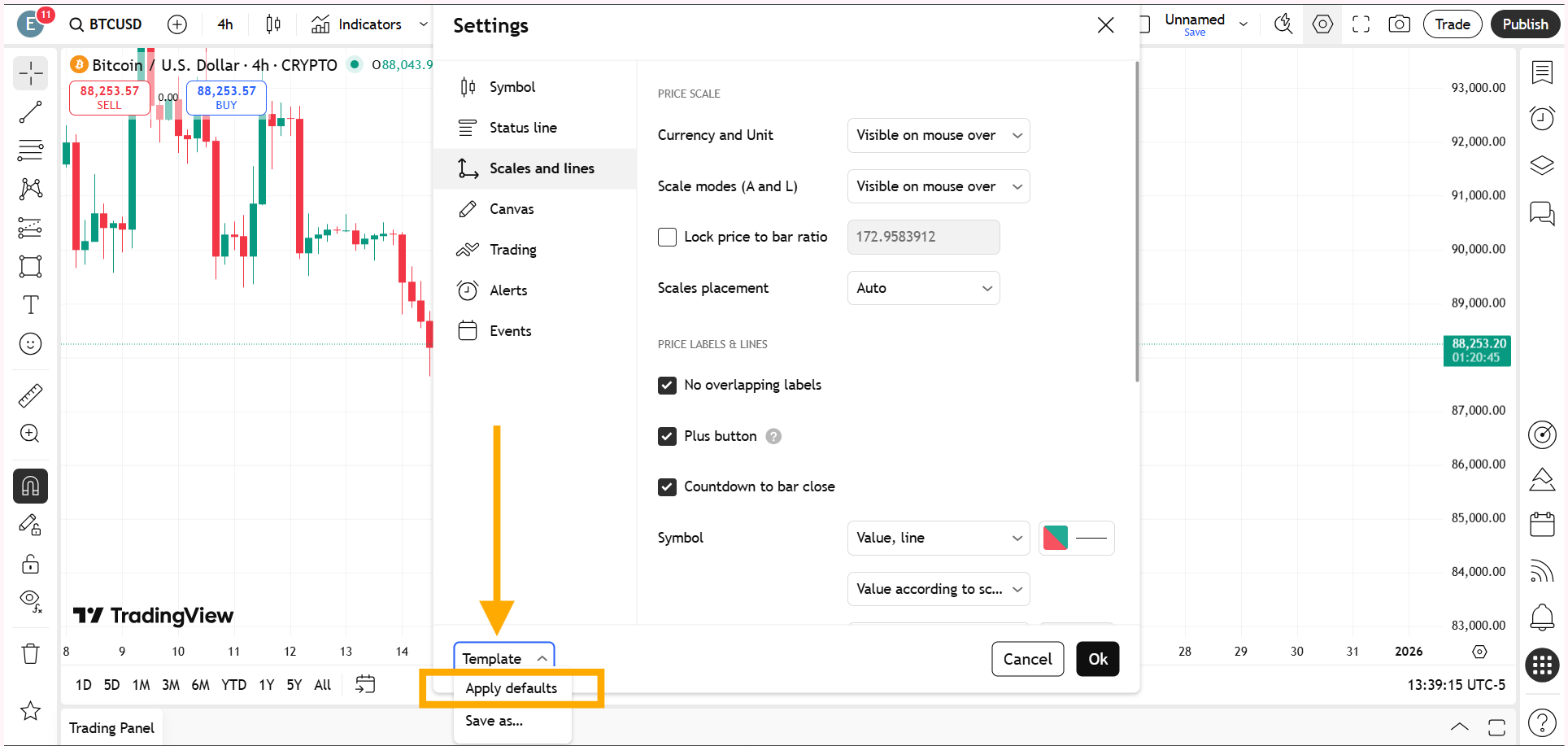
Since the Countdown to Bar Close is part of TradingView’s default chart setup, resetting the chart automatically restores the timer along with other standard visual settings.
By reverting the chart to its original state, all hidden or disabled features, including the candlestick close timer, become visible again.
While this approach may remove some customizations, it provides the fastest solution when troubleshooting becomes confusing or time-consuming.
Also Read – Candlesticks Not Showing or Visible in TradingView? – Complete Solution Guide
Which Method Should You Use?
All the methods ultimately lead to the same result, but the choice depends on the trader’s specific situation.
If the chart is heavily customized and only the timer is missing, manually enabling the ‘Countdown to Bar Close’ is the better option.
On the other hand, if multiple chart elements are behaving unexpectedly or the cause of the missing timer is unclear, resetting the chart to default can save time and effort.
For a better understanding, watch the full video below.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Investing in stocks, cryptocurrencies, or other assets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Always conduct your own research or consult a qualified financial advisor before making investment decisions. The author and publisher are not responsible for any financial losses incurred from actions based on this article. While efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, economic data and market conditions can change rapidly. The author and publisher do not guarantee the completeness or accuracy of the information and are not liable for any errors or omissions. Always verify data with primary sources before making decisions.
What time do the 4 hour candles close?
The answer is already contained in the question itself. A 4-hour candlestick closes exactly four hours after it opens. After every four hours, the current candle closes and a new 4-hour candle begins, which will again close after the next four hours. This happens only when the selected timeframe is set to 4H.
On TradingView, you can check the remaining time for a candle to close on the right-side price scale by enabling the candle close timer. This shows how much time is left before the current 4-hour candle closes.