Blockchain is like a shared digital notebook that records all cryptocurrency transactions. No one can change entries alone. In this article we will cover key ideas and keywords such as blockchain how to create, components of blockchain, block chain images, and more.
Table of Contents
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is like a shared digital notebook that records transactions securely across many computers (called nodes). No single person or company controls it, making it decentralized and tamper-proof.
Blockchain is like a chain of blocks. Each block holds some data. The data can be transactions or contracts. Every block links to the one before it. This link is very strong. It is made by math codes. No one can change a block without breaking the chain. The chain lives on many computers at once. This makes it safe and open.
Blockchain in Cryptocurrency like Bitcoin
Take Bitcoin as an example. Every time someone sends Bitcoin, the transaction goes into a block. The block joins the chain. Once it is there, no one can erase it. This stops a person from spending the same Bitcoin twice. Everyone on the network sees the transaction. This builds trust. It helps stop scams and tricks.
Blockchain ensures every transaction is transparent and permanent.
What Does Decentralization Mean?
Decentralization means no single person is in charge. Many computers share the work. Each computer has a full copy of the chain. If one computer stops, the others keep going. This makes the system strong. It has no single weak point. Public blockchains like Bitcoin are very decentralized. Private blockchains used by companies may have fewer computers. They are less open but still help many users.
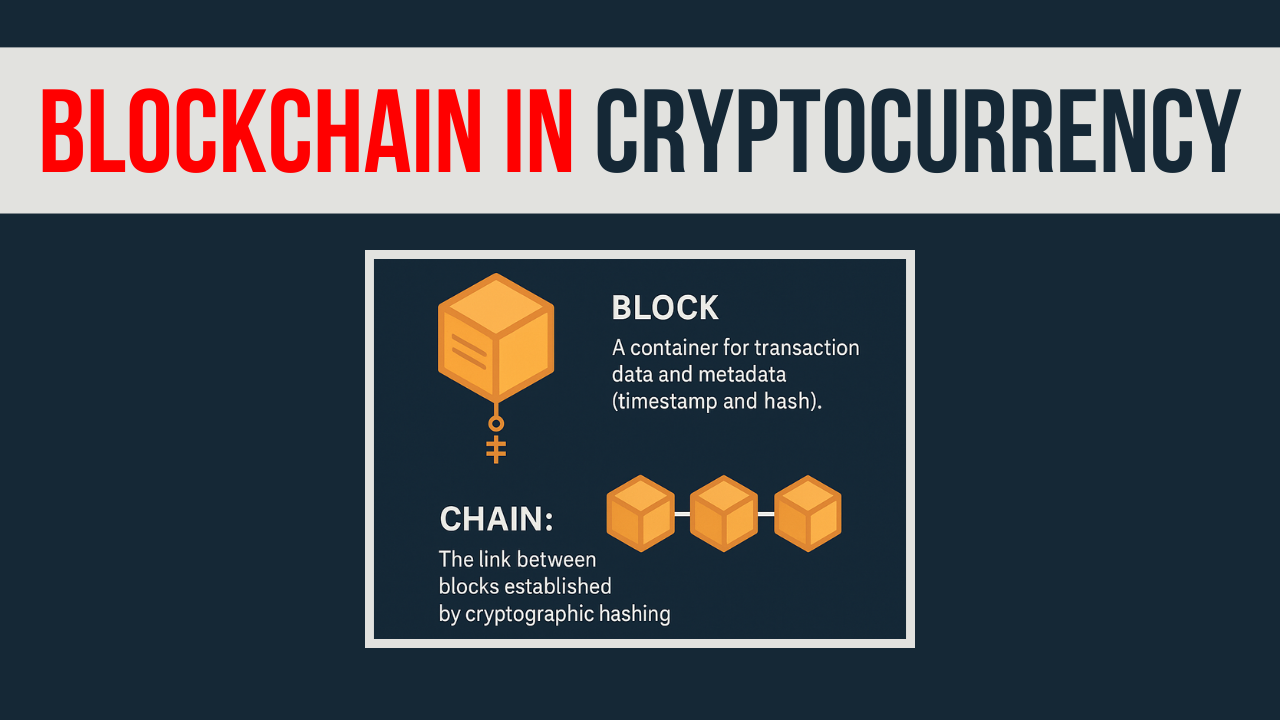
Key Components of Blockchain
- Block: A digital “page” that stores transaction details (amounts, sender/receiver) and a timestamp.
- Chain: Blocks are linked using unique codes (hashes), forming a secure chain. Changing one block breaks the entire chain.
- Nodes: Computers worldwide that store copies of the blockchain, ensuring no single point of failure.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Rules like Proof of Work (used by Bitcoin) or Proof of Stake that help nodes agree on valid transactions.
How Does Blockchain Work in Cryptocurrency?
- Step 1: A user initiates a transaction (e.g., sending Bitcoin).
- Step 2: Nodes verify the transaction using pre-set rules.
- Step 3: Verified transactions are grouped into a block.
- Step 4: The block gets a unique hash and is added to the chain.
- Step 5: All nodes update their copies of the blockchain.
This process ensures security (no fraud) and transparency (everyone sees the same records).
Also Read – Does Cryptocurrency Have a Future in India?
Where Is Blockchain Stored?
Blockchain isn’t stored in one place. Instead:
- Every node keeps a full copy.
- There’s no central server—data is spread globally.
Who Invented Blockchain?
The concept of blockchain technology was introduced in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto (a person or group) through the Bitcoin whitepaper. Since then, blockchains like Ethereum expanded the technology for uses beyond payments.
Real-World Uses of Blockchain in Cryptocurrency
1. Digital Payments
Blockchain enables fast, low-cost global money transfers without relying on banks or payment processors.
- Example: Sending Bitcoin from Japan to Brazil takes minutes, with fees as low as a few cents. Traditional methods like bank transfers can take days and charge high fees.
- How it works: Transactions are verified by nodes worldwide, cutting out middlemen. This is especially useful for migrant workers sending remittances to families.
2. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi platforms use blockchain to recreate financial services (loans, savings, trading) without banks.
- Example: On platforms like Aave or Compound, you can:
- Lend crypto and earn interest daily (no bank account needed).
- Borrow funds instantly by using crypto as collateral.
- Benefits: Open 24/7 to anyone with an internet connection, even in regions with no banks.
3. NFTs & Digital Art
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) use blockchain to prove ownership of unique digital items.
- Example: Artists sell digital art as NFTs (e.g., Beeple’s $69 million artwork). Buyers get a blockchain certificate that can’t be copied.
- Use cases:
- Collectibles: Rare in-game items, virtual land (e.g., Decentraland).
- Royalties: Artists earn automatic commissions every time their NFT is resold.
Why Is Blockchain Important?
No Middlemen
- Direct transactions: You can send money, sign contracts, or trade assets directly with others. No banks, lawyers, or brokers are needed.
- Cost savings: Eliminating intermediaries reduces fees (e.g., sending 10,000viaBitcoincosts 10,000viaBitcoincosts 1 vs. ~$500 via traditional services).
Security
- Tamper-proof records: Each block is linked to the previous one using cryptography. To hack a blockchain, you’d need to alter every copy on all nodes—nearly impossible.
- Example: Bitcoin’s blockchain has never been hacked since 2009.
Transparency
- Public ledger: Anyone can view all transactions (e.g., explore Bitcoin’s blockchain on Blockchain.com).
- Trustless system: You don’t need to trust a bank—verify transactions yourself using the blockchain’s open records.
Latest Developments in Blockchain Technology
Here are the latest developments in blockchain technology, explained in simple language:
- Tokenizing Real-World Assets
Organizations are creating digital tokens that represent ownership in real items such as real estate, art, or gold. This allows more people to invest by buying small shares of valuable assets. - Combining AI with Blockchain
Artificial intelligence is being used together with blockchain to make systems smarter. For example, AI can detect fraud in transactions or automate tasks on decentralized platforms. - Enhanced Privacy with Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Zero-knowledge proofs let users prove information without revealing the actual data. This makes blockchain transactions more private and secure. - Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Some governments are creating their own digital money. For example, the digital rupee can work offline. This helps people make digital payments even without an internet connection. - Eco-Friendly Blockchain Practices
Blockchain networks are moving from energy-heavy methods to more efficient ones like Proof of Stake. This reduces power use and lowers the carbon footprint. - Modular Blockchain Infrastructure
Modular blockchains work like building blocks that developers can mix and match. This makes it easier to build custom solutions that are faster and more efficient. - Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
DAOs are groups that make decisions together without a central leader. They use blockchain to vote and manage projects, offering more transparency and fairness. - Clearer Regulations for Digital Assets
Governments are developing laws to regulate cryptocurrencies and other digital assets. Better rules help protect users and promote innovation. - Big Tech Embracing Blockchain
Large companies are adding blockchain features to their services. For example, some are exploring digital payments using stablecoins and improving cross-border transactions. - Blockchain in Gaming and the Metaverse
Blockchain lets players own and trade in-game items outside the game. This creates real value for virtual goods and new opportunities in online gaming economies.
First Country in the World to Use Blockchain
In April 2016, Georgia became the first nation to use blockchain for a government land registry. Partnering with Bitfury, it used the Bitcoin blockchain to record property titles. This helped ensure transparency and reduced fraud.
By 2017, the project expanded and became a global example. Unlike regular systems, blockchain created tamper-proof records. Although Sweden and Estonia later explored similar ideas, Georgia’s effort in 2016 was the earliest. This step showed how blockchain could improve public systems and inspired other countries to try the same.
Government of India’s Dedicated Blockchain Section
The Government of India has launched a dedicated blockchain portal, blockchain.gov.in, under the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY) and the National Informatics Centre (NIC). The platform, part of the Centre of Excellence (CoE) in Blockchain Technology, hosts nearly 8 million documents across five blockchains, including certificate, property, and drug logistics chains. It features case studies and dashboards showcasing projects like land records and GST enforcement.
It offers Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) to enable businesses and government entities to deploy blockchain solutions efficiently. The portal also gives easy guides about parts of blockchain and offers tutorials for developers. This helps in creating new ideas and building skills for improving online government services and public facilities.
Also Read – 5 Benefits of Cryptocurrency for Governments Around the World
Conclusion
Blockchain is the backbone of cryptocurrency. It’s a secure, shared digital ledger that eliminates the need for central control. By linking blocks of data across thousands of computers, it ensures trust and transparency—making it revolutionary for finance, contracts, and beyond.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational and educational purposes only and is not financial advice. It is written in good faith and with reasonable care, but we cannot guarantee its accuracy or completeness. Readers should consult a professional advisor before taking action. We are not liable for any losses arising from this content. Updates will be made as needed.