The latest US CPI data for August 2025 from the Bureau of Labor Statistics shows that headline CPI, which tracks changes in the prices of a broad basket of goods and services, rose 0.4 percent in August after a 0.2 percent increase in July, bringing the year-over-year rate to 2.9 percent.
The main contributors were shelter, food, and energy, with gasoline prices seeing a notable 1.9 percent rise.
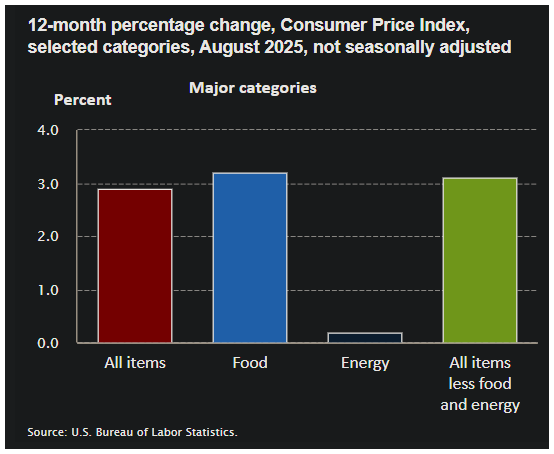
Meanwhile, Core CPI – which excludes the more volatile food and energy components – rose 0.3 percent in August, matching July’s pace. On a yearly basis, Core CPI increased 3.1 percent, highlighting that underlying inflationary pressures, particularly from categories like airline fares, used cars, apparel, and new vehicles, remain firm even as some areas such as medical care and recreation eased.
The CPI report today shows that overall inflation pressures remain steady but slightly higher than in July.
As per the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the September 2025 CPI data release is scheduled for October 15, 2025, at 8:30 A.M. Eastern Time. Investors, traders, and policymakers will closely watch it to confirm whether inflation continues to stabilize or re-accelerates.
Also Read – August 2025 PPI Report Explained – What It Means for Inflation, CPI, and Fed Rate Cuts?
Inflation July 2025 Versus August 2025 USA
The change from July 2025 inflation versus August 2025 USA shows a clear acceleration in the monthly pace of price increases. July’s 0.2 percent rise was modest, while August doubled to 0.4 percent.
This indicates that inflation is stabilizing but remains above the Federal Reserve’s target.
CPI Variation from August 2022 to August 2025
From August 2022 to August 2025, U.S. CPI has shown significant variation, reflecting post-pandemic recovery and policy shifts.
In August 2022, headline inflation peaked near 8.3 percent amid supply chain disruptions and energy spikes. By August 2025, it moderated to 2.9 percent, a cumulative decline of about 5.4 percentage points, though still above the Fed’s target.
Core CPI eased from around 6.3 percent in 2022 to 3.1 percent in 2025, a 3.2-point drop, driven by falling energy prices and supply normalization.
Over the three-year period, inflation averaged roughly 4.5 percent annually, with 2022’s surge (9.1 percent peak) contrasting with the 2.7-2.9 percent range in 2024–2025. This cooling trend was influenced by Fed rate hikes and tariff uncertainties, while recent upticks have been tied to external factors like trade policies.
CPI Data and Federal Reserve Rate Cut Debate
Markets are now asking – Will the Fed cut rates in September 2025?
With inflation cooling compared to the highs of 2022 but still running above target, this question has become more urgent. The Federal Reserve is closely monitoring this inflation report alongside jobless claims and wage growth.
Expectations remain strong for a 25 basis-point rate cut at the September FOMC meeting. The probability of a larger 50 basis-point cut has diminished slightly after the hotter-than-expected CPI data today. Still, the broader trend – combined with weakening job data – suggests the Fed is likely to move toward easing.
Also Read – Fed Interest Rates vs Gold Prices – What to Expect Ahead of the September 2025 FOMC Meeting?
How does CPI affect gold prices?
CPI measures inflation. When inflation is higher, gold often rises because it is seen as a hedge. If the Fed cuts rates after high CPI, gold demand usually increases further.
Does CPI data affect Bitcoin price movements?
CPI affects Bitcoin prices indirectly through monetary policy. When CPI is higher than expected, the Federal Reserve may delay interest rate cuts, which can hurt crypto markets in the short term. On the other hand, when CPI is stable or lower, it increases the chances of rate cuts, making risk assets like Bitcoin more attractive and often pushing prices higher.
What is the effect of CPI on the stock market?
If CPI data is high, stocks may face pressure due to fears of delayed rate cuts. But if inflation is stable and the Fed cuts rates, equities often benefit.
How does CPI make the Fed adjust interest rates?
The Fed’s dual mandate is price stability and employment. CPI data signals whether inflation is near or above the target. Higher inflation can keep rates elevated, while stabilizing or falling inflation encourages cuts.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Investing in stocks, cryptocurrencies, or other assets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Always conduct your own research or consult a qualified financial advisor before making investment decisions. The author and publisher are not responsible for any financial losses incurred from actions based on this article. While efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, economic data and market conditions can change rapidly. The author and publisher do not guarantee the completeness or accuracy of the information and are not liable for any errors or omissions. Always verify data with primary sources before making decisions.

